PCB Capacities and Technical Specification | |
Order Quantity | 1-500,000 |
Layer | 1, 2, 4, 6, up to 24 layer |
Materia | FR-4, High Tg, Isola, Aluminum, Rogers, etc |
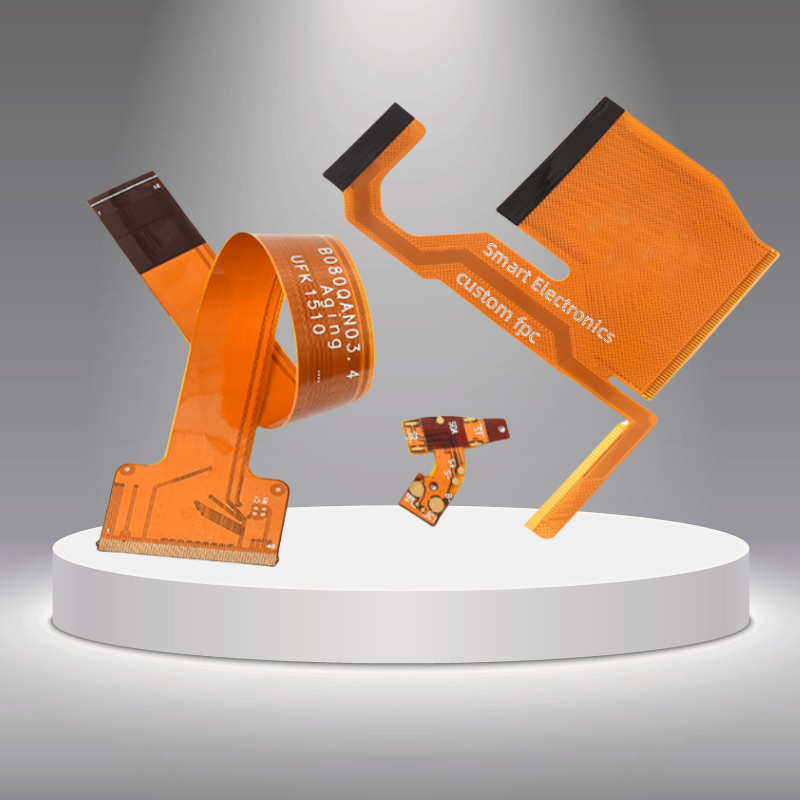
PCB type | Rigid, flexible, rigid-flexible |
Shape | Rectangular, round, slots, cutouts, complex, irregular |
Max PCB dimensions | 1200mm*600mm |
Thickness | 0.2~4.0mm, Flex 0.01~0.25'' |
Thickness tolerance | ± 10% |
Copper thickness | 0.5-6 oz |
Copper thickness tolerance | ± 0.25oz |
Surface finish | HASL, LF HASL, Imm Gold, Imm Silver, OSP etc |
Solder mask | Green, red, white, yellow, blue, black, orange, purple |
Silk screen | White, black |
Silk screen min line width | 0.006'' or 0.15mm |
Min drill hole diameter | 0.01'', 0.1mm or 10 mil |
Min trace/gap | 0.075mm or 3mil |
PCB cutting | Shear, V-score, tab-routed |
PCBA Capabilities | |
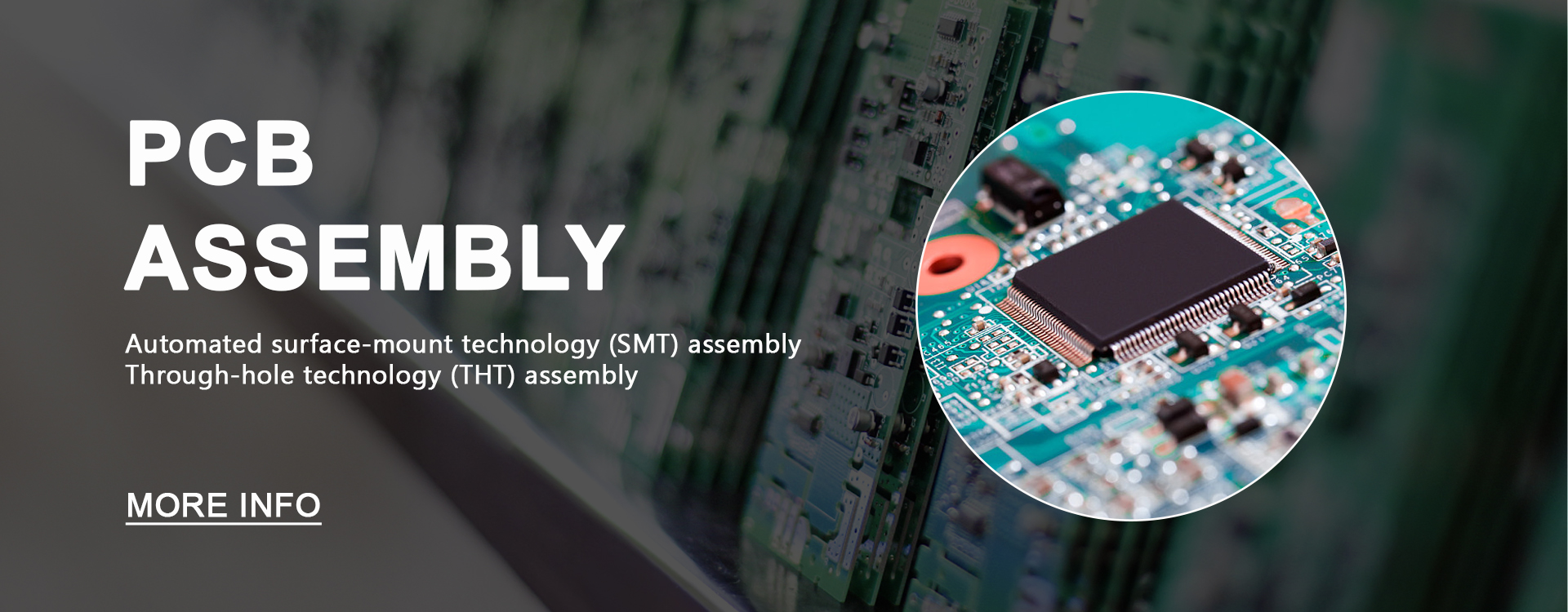
Turnkey PCBA | PCB+components sourcing+assembly+package |
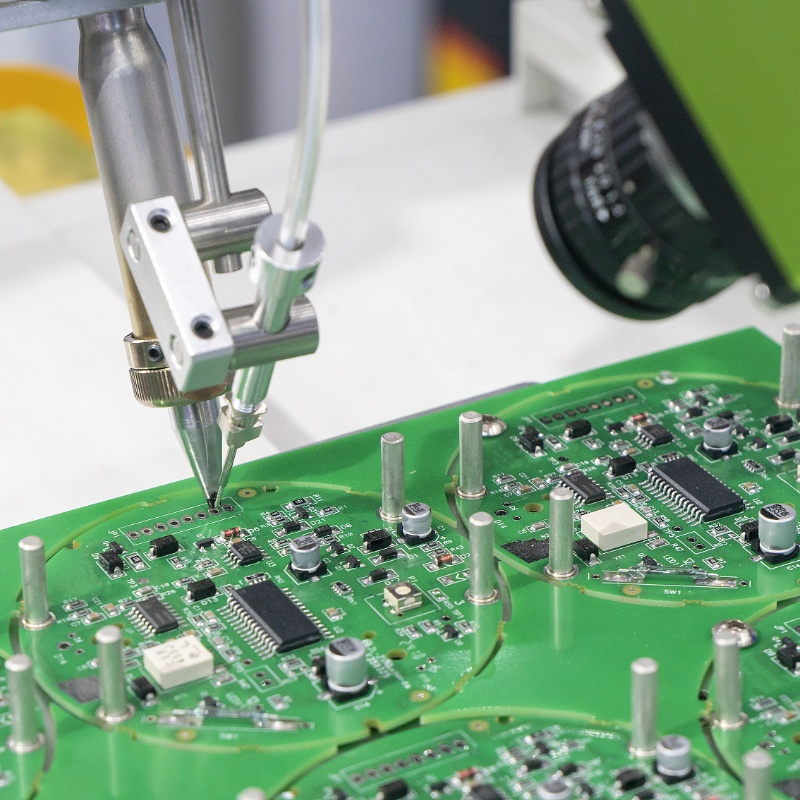
Assembly details | SMT and Thru-hole, ISO SMT and DIP lines |
Lead Time | Prototype : 15 work days. Mass order : 20~25 work days |
Testing on products | Testing jig/mold , X-ray Inspection, AOI Test, Functional test |
Quantity | Min quantity : 1pcs. Prototype, small order, mass order, all OK |
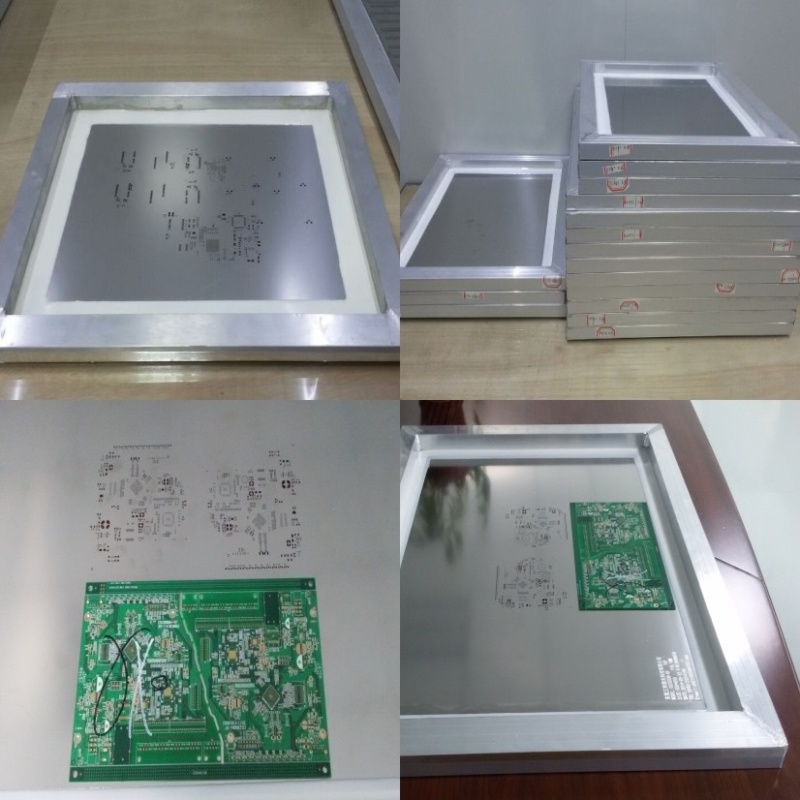
Files needed | PCB : Gerber files(CAM, PCB, PCBDOC) Components : Bill of Materials(BOM list) Assembly : Pick-N-Place file |
PCB Panel Size | Min size : 0.25*0.25 inches(6*6mm) Max size : 1200*600mm |
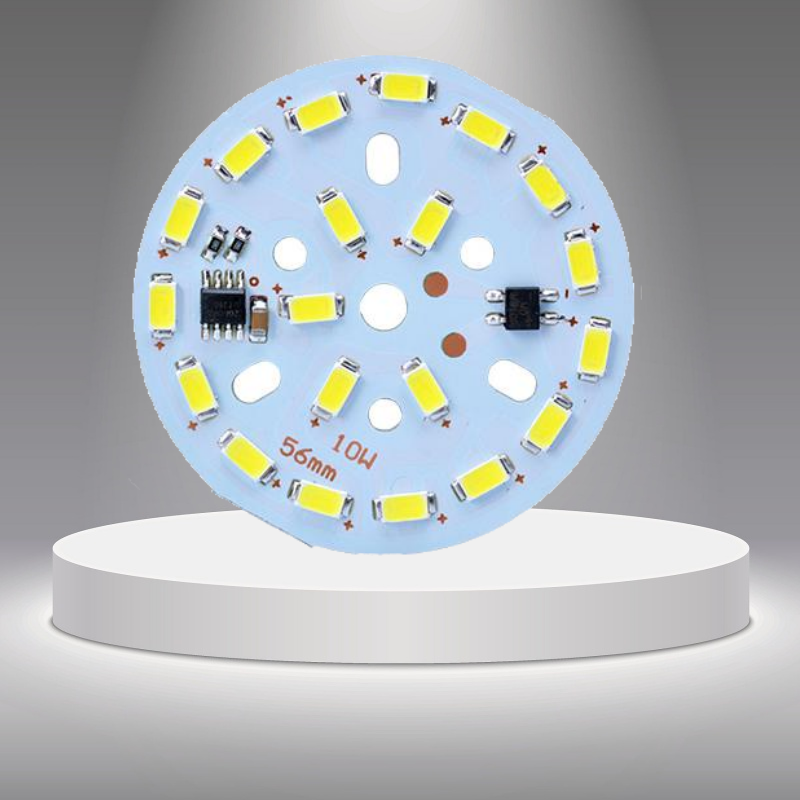
Components details | Passive Down to 0201 size BGA and VFBGA Leadless Chip Carriers/CSP Double-sided SMT Assembly Fine Pitch to 0.8mils BGA Repair and Reball Part Removal and Replacement |
Component package | Cut Tape, Tube, Reels, Loose Parts |
PCB+ assembly process | Drilling---Exposure---Plating--- Etaching & Stripping---Punching---Electrical Testing---SMT---Wave Soldering---Assembling---ICT--- Function Testing---Temperature &Humidity Testing |